BufferedWriter
public class Ex05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("test04.txt");
Writer fw = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try {
fw = new FileWriter(file);
bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
bw.write("문자열버퍼를 이용해 작성할 예정입니다.");
bw.flush(); // 버퍼 비워내기 안써도 close 할때마다 밀어내서 저장을 한다.
// 실시간 통신의 경우 close 없이 메세지를 전달해야하기 떄문에 flush를 해줘야한다.
// bw.write("\r\n");
bw.newLine(); // 운영체제에 맞게 개행해줌
bw.write("또 한줄 더 작성하겠습니다.");
if(bw!=null) bw.close();
if(fw!=null) fw.close();
System.out.println("작성완료");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
BufferedReader
public class Ex06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("test04.txt");
Reader fr = null;
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
fr = new FileReader(file);
br = new BufferedReader(fr);
// int su = -1;
// while((su=br.read()) != -1) {
// System.out.print((char)su);
// }
String msg = null;
while((msg=br.readLine())!=null) {
System.out.println(msg);
}
if(br!=null)br.close();
if(fr!=null)fr.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
PrintWriter
public class Ex07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Writer fw = null;
PrintWriter pw = null;
try {
fw = new FileWriter(new File("test07.txt"));
pw = new PrintWriter(fw);
pw.print(true);
pw.print(1234);
pw.print(3.14);
pw.println();
pw.println("문자열 메세지 작성");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if(pw!=null) pw.close();
if(fw!=null) fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
finally
public class Ex08 {
public static void func01() {
System.out.println("func start");
try {
int a = 4, b = 0, c = a / b;
System.out.println(c);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
} finally {
// 반드시 실행됨
System.out.println("func end");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
func01();
}
}
Auto close
public class Ex09 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Auto close
// jdk 1.8 이상 try의 ()안에 들어 갈 수 있는 클래스는 Closable을 구현한 객체들만 가능
// ()안에 있는 객체들은 자동으로 close 해준다. 반드시 선언도 괄호 안에서 되어야한다.
try (Reader reader = new FileReader("test07.txt");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader)){
String msg = null;
while ((msg = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(msg);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.getStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.getStackTrace();
}
}
}
OutputStreamWriter
public class Ex10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
OutputStream os = null;
Writer osw = null;
try {
os = new FileOutputStream("test08.txt"); // exist 판별안해도 알아서 새로 생성해주고 덮어쓴다.
osw = new OutputStreamWriter(os);
osw.write("문자열 작성합니다.");
if(osw!=null) osw.close();
if(os!=null) os.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
InputStreamReader
public class Ex11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream is = null;
Reader isr = null;
try {
is = new FileInputStream("test08.txt");
isr = new InputStreamReader(is);
int su = -1;
while((su=isr.read())!=-1) {
System.out.print((char)su);
}
if(isr!=null) isr.close();
if(is!=null)is.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Thread 제어(간접제어, 직접제어)
간접제어
public class Ex12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Thread thr = new Thread() {
// @Override
// public void run() {
// System.out.println("New Thread start");
// try {
// Thread.sleep(3000);
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// System.out.println("New Thread end");
// }
// };
// thr.start();
// thr.start(); IlleagalThreadStateException 발생!
Runnable thr = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Thread thr = Thread.currentThread();
int su = thr.getPriority(); // 스레드 우선순위
System.out.println(thr.getName() +" New Thread start..." + su);
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(thr.getName() +" New Thread end..." + su);
}
};
Thread thr1 = new Thread(thr);
Thread thr2 = new Thread(thr);
thr1.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); // 1 ~ 10 까지 normal 5 max 10 min 1 상대적 빈도수일뿐 무조건적인건 아니다.
thr2.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
thr1.start();
thr2.start();
}
}
직접제어
class Lec13 extends Frame implements Runnable{
Label la = new Label();
public Lec13() {
add(la);
setBounds(100, 100, 300, 150);
setVisible(true);
}
public void loading() {
while(true) {
la.setText(new Date().toString());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
loading();
}
}
public class Ex13 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Thread 직접 제어
Lec13 me = new Lec13();
Thread thr = new Thread(me);
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true) {
System.out.print("1.시작 2.멈춤 3.재시작 4.종료 0.끝>");
int input = sc.nextInt();
if(input == 0) break;
if(input == 1) thr.start();
if(input == 2) thr.suspend();
if(input == 3) thr.resume();
if(input == 4) thr.stop();
}
}
}Thread의 life cycle
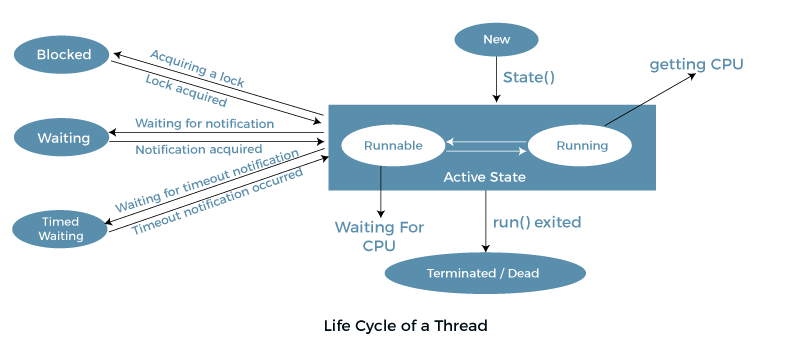
Thread 제어
join()
해당 쓰레드가 끝날 때 까지 다른 쓰레드를 기다리게한다. 매개변수로 주는 시간은 최대 대기 시간이며 해당 시간이 지나면 다른 쓰레드의 waiting 상태가 풀린다.
public class Ex02 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(getName() + " start...");
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(getName() + " end...");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("main start...");
Ex02 me = new Ex02();
me.start();
try {
// join 해당 스레드가 끝날 때 까지 대기함 - waiting 상태로 빠짐. 매개변수는 최대로 대기하는 시간
me.join(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("main end...");
}
}
interrupt()
sleep중인 Thread를 깨우는 것 더 정확히는 해당 함수 호출 시 InterruptException을 발생시킨다. 이후 catch에서 추가 작업을 할 수 있다.
public class Ex03 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println(getName() + "working..");
try {
Thread.sleep(10000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ex03 me = new Ex03();
Ex03 you = new Ex03();
me.start();
you.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
you.interrupt();
}
}
yield()
단어 그대로 작업 순위를 양보하는 것, 해당 쓰레드를 실행하지않고 runnable로 다시 되돌리는 것 확률적인 것이기 때문에 100% 양보는 안된다.
class Lec04 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(getName() + " working...");
}
}
}
public class Ex04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Lec04 ex1 = new Lec04();
Lec04 ex2 = new Lec04();
ex1.start();
ex2.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
ex1.yield();
}
}
}
synchronized
같은 객체에 접근할 때 동시성 문제가 발생하는데 해당 키워드를 이용해서 병렬작업을 시행할 때 겪는 동시성 문제를 막아 준다.
class Lec05 extends Thread {
int su1, su2;
static int sum = 0;
Object key;
public Lec05(int su1, int su2, Object key) {
this.su1 = su1;
this.su2 = su2;
this.key = key;
}
public void hap(int su1, int su2) {
for (int i = su1; i <= su2; i++) {
synchronized(this) {// key로 사용될 공통의 객체가 필요하다.
sum = sum + i;
}
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
hap(su1,su2);
System.out.println(su1 + "~" + su2 + "=" + sum);
}}
public class Ex05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ex05 key = new Ex05();
// synchronized를 위해 공통의 객체를 전달
Lec05 lec1 = new Lec05(1, 5000, key);
Lec05 lec2 = new Lec05(5001, 10000, key);
// lec1.start();
// lec2.start();
// 하나의 객체일 때 synchronized에 this를 사용할 수 있다.
Thread thr1 = new Thread(lec1);
Thread thr2 = new Thread(lec1);
thr1.start();
thr2.start();
}
}
wait() notify()
Object가 가지고 있는 메서드들인데 이들을 통해서 제어 할 수 있다. 다만 synchronized를 반드시 써야한다. 쓰지않으면 IllegalMoniterStateException 발생한다.
class Lec06 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
synchronized (this) {
System.out.println(i+1+"번 수행...");
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(i > 1)notify(); // 최소 2번은 실행하고 깨우기
}
}
}
}
public class Ex06 {
/*
* Object의 wait() notify() 메서드들로 쓰레드를 제어할 수 있다.
* 대신 synchronized를 사용하지않으면 IllegalMoniterStateException이 발생한다.
* Interrupte를 통해서는 특정 쓰레드만 깨울 수 있도록 제어 가능하나
* nofityAll()은 무조건 전부를 깨움
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("main start");
Lec06 lec = new Lec06();
lec.start();
synchronized (lec) {
try {
lec.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("main end");
}
}
setDaemon()
부모쓰레드에 종속되도록 설정 -> 부모쓰레드가 죽으면 같이 죽음
class Lec08 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
while(true) {
System.out.println("running...");
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public class Ex08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("main start...");
Lec08 me = new Lec08();
me.setDaemon(true); // 종속시킴으로써 main이 죽을 때 같이 죽음
me.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("main end...");
}
}
Thread는 코드로 직접제어 하는게 제일 좋다.
class Lec07 extends Thread {
boolean boo = true; // 쓰레드 실행 종료 제어
boolean boo2 = false; // 쓰레드 일시 정지, 시작 제어
@Override
public void run() {
while (boo) {
if(boo2) {
System.out.println("working");
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
yield();
}
}
}
}
public class Ex07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Lec07 me = new Lec07();
me.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
me.boo2 = true;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
I/O - Object Stream
ObjectOutputStream
public class Ex09 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Object Stream
OutputStream out = null;
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
out = new FileOutputStream("data09.bin");
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(out);
oos.writeInt(1234);
oos.writeDouble(3.14);
oos.writeBoolean(true);
oos.writeUTF("문자열");
int[] arr1 = {1,3,5,7,9};
oos.writeObject(arr1);
Vector arr2 = new Vector();
arr2.add(1234);
arr2.add(3.14);
arr2.add(true);
arr2.add('a');
arr2.add("가나다");
oos.writeObject(arr2);
ArrayList arr3 = new ArrayList();
arr3.add(4434);
arr3.add(1.11);
arr3.add(false);
arr3.add("ArrayList");
arr3.add('Z');
oos.writeObject(arr3);
HashSet arr4= new HashSet();
arr4.addAll(arr3); // 깊은복사
arr4.add(arr3); // 객체를 넣음
oos.writeObject(arr4);
if(oos!=null)oos.close();
if(out!=null)out.close();
System.out.println("작성..");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
ObjectInputStream
public class Ex10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream in = null;
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
in = new FileInputStream("data09.bin");
ois = new ObjectInputStream(in);
int su = ois.readInt();
double su2 = ois.readDouble();
boolean boo = ois.readBoolean();
String msg = ois.readUTF();
// Object obj1 = ois.readObject();
// Object obj2 = ois.readObject();
int[] arr1 = (int[])ois.readObject();
Vector arr2 = (Vector)ois.readObject();
ArrayList arr3 = (ArrayList)ois.readObject();
HashSet arr4 = (HashSet)ois.readObject();
System.out.println(su);
System.out.println(su2);
System.out.println(boo);
System.out.println(msg);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr1));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2.toArray()));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr3.toArray()));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr4.toArray()));
if(ois!=null)ois.close();
if(in!=null)in.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
자료구조가 아닌 객체를 ObjectStream 할 경우 Serializable 인터페이스를 상속받아야한다.
ObjectOutputStream
class Lec11{ // Seiralizable을 상속받아 구현해야만 I/O를 통해 객체를 보낼 수 있다.
int su = 1234;
public void func() {
System.out.println("func run - "+ su);
}
}
class Lec111 implements Serializable{
// Serializable 을 구현한 객체는 UUID형태로 시리얼버젼이 붙게되는데 이를 통해서 구분하기 때문에 소스코드를 수정하면 오류가 발생하기 쉽다.
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; // 버젼을 바꾸게되면 InvalidClassException이 발생한다.
int su = 1234;
transient int su2 = 2222; // 값이 전달되지않도록 함 default값 출력
private int su3 = 3333;
public void func1() { // 메소드는 Serializable의 대상이 아니다.
System.out.println("func1 run - su2:"+ su2);
System.out.println("func1 run - su3:"+ su3);
}
}
public class Ex11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
OutputStream out = null;
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
out = new FileOutputStream("data11.bin");
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(out);
// Lec11 lec = new Lec11();
// oos.writeObject(lec); // NotSerializableException 발생!
Lec111 lec = new Lec111();
oos.writeObject(lec);
if(oos!=null)oos.close();
if(out!=null)out.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
ObjectInputStream
public class Ex12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream in = null;
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
in = new FileInputStream("data11.bin");
ois = new ObjectInputStream(in);
// Object obj = ois.readObject();
while(true){
Lec111 obj;
try {
obj = (Lec111)ois.readObject();
} catch (EOFException e) {
break;
}
System.out.println(obj.su);
System.out.println(obj.su2); // transient가 걸려있기 때문에 값 전달이 되지 않는다.
// System.out.println(obj.su3); // private은 접근자체가 불가능하나
obj.func1(); // 함수에선 전달되는 것을 확인 할 수있다.
}
if(ois!=null)ois.close();
if(in!=null)in.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}통신
IP
원격으로 pc에 접속하기 위해선 ip가 필요하다 ip는 (1byte x 4)의 체계를 갖추고 있다.
ip는 0~255까지 정수 4자리로 이루어져 있다. ipv6은 주소로 16진수 4자리수 ipv9도 있긴한데 중국에서만 사용한다.
공인IP - 진짜IP 인터넷에서 사용자 식별을 위한 IP
사설IP - 공유기에 묶여서 등장하는 IP와 같이 별도의 네트워크에서 사용되는 IP, 외부에서 접근은 불가능하며 중복이 가능하다.
유동IP
개인사용자를 위해서 임의의 비어있는 ip를 받아 사용하는 것 가정에서는 사설IP면서 유동IP 인 것
자동으로 게이트웨이, 서브넷마스크, DNS를 자동할당 해줘서 인터넷과 연결하기 쉽도록 해주는게 DHCP 서버이다.
일반적으로 공유기가 해당 기능을 수행해줌
고정IP
학교,회사 등 관공서에서는 DHCP를 지원하지 않기 때문에 직접 설정을 해줘야 인터넷을 사용 할 수 있게 된다.
게이트웨이, DNS, 서브넷 마스크를 직접 기입 해줘야 인터넷을 사용 할 수 있다.
또한 변경되어서도 안되기 때문에 고정 IP를 이용해야한다.
DNS - Domain Name Server
원칙은 ip를 통해서 접속해야하는 것이 맞으나 전부 기억할 수 없기에
Domain을 지정해서 naver.com와 같은 값을 입력하여 해당 pc에 접속 할 수 있도록 함.
naver.com을 입력하는 순간 DNS에 해당 이름을 찾아 달라고 요청하는데
그러면 DNS에서 ip를 알려주고 우리는 받은 ip를 통해 네이버에 접속할 수 있게 되는 것
DNS서버의 주소는 통신사를 무엇을 사용하느냐에 따라 달라지게된다.
host
windows의 hosts파일에 저장되어있는 Domain과 ip가 있을 경우 DNS서버에 가서 안물어보고 바로 해당 ip로 가게 된다.
이를 이용하여 hosts 파일을 위변조하여 피싱사이트에 접속되도록 할 수 있게 된다.
그렇기에 공용으로 사용되는 컴퓨터에서 모든 내용을 100% 신뢰하기 어렵게 된다.
InetAddress
public class Ex01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
java.net.InetAddress addr1 = null;
java.net.InetAddress addr2 = null;
java.net.InetAddress addr3 = null;
// addr1 = new InetAddress(); // default 생성자가 없다.
try {
// 도메인 이름을 통한 연결
addr1 = InetAddress.getByName("naver.com");
System.out.println(addr1.getHostName()); // naver.com
System.out.println(addr1.getHostAddress()); // 223.130.195.95
System.out.println("======");
// IP를 통한 연결 (ipv4) - (1byte x 4) 의 체계를 갖추고 있다.
byte[] arr1 = {(byte)223,(byte)130,(byte)195,95}; // byte배열을 받음
addr2 = InetAddress.getByAddress(arr1);
System.out.println(addr2.getHostAddress());
System.out.println("======");
// 내 ip 192.168.240.119
// byte[] arr2 = {(byte)192,(byte)168,(byte)240,119};
byte[] arr2 = {127,0,0,1}; // localhost
// addr3 = InetAddress.getByAddress(arr2);
// addr3 = InetAddress.getByName("DESKTOP-O5AJ5VH");
addr3 = InetAddress.getByName("localhost");
System.out.println(addr3.getHostName());
System.out.println(addr3.getHostAddress());
System.out.println("======");
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
URL
public class Ex03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// URL vs URI
// 프로토콜://도메인:포트번호/경로/../경로?쿼리스트링#ref(앵커)
String msg = "";
msg = "https://namu.wiki/w/%EB%A7%A4%EB%8B%88%20%ED%8C%8C%ED%80%B4%EC%95%84%EC%98%A4#s-8";
java.net.URL url = null;
try {
url = new URL(msg);
System.out.println("protocol : " + url.getProtocol());
System.out.println("domain : " + url.getHost());
System.out.println("port : " + url.getPort());
System.out.println("default port : " + url.getDefaultPort());
System.out.println("file : " + url.getFile());
System.out.println("path : " + url.getPath());
System.out.println("queryString : " + url.getQuery());
System.out.println("ref : "+ url.getRef());
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
웹크롤링
public class Ex04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("7zip.exe");
URL url = null;
InputStream is = null;
// InputStreamReader isr = null;
// BufferedReader br = null;
//byte stream
OutputStream os = null;
// 문자열인 경우
// Writer fw = null;
// PrintWriter pw = null;
try {
os = new FileOutputStream(file);
// fw = new FileWriter(file);
// pw = new PrintWriter(fw);
url = new URL("https://www.7-zip.org/a/7z2201-x64.exe");
URLConnection conn = url.openConnection();
is = conn.getInputStream();
// isr = new InputStreamReader(is);
// br = new BufferedReader(isr);
// String msg = null;
// while((msg=br.readLine())!=null){
// os.(msg);
// }
int su = -1;
while((su=is.read())!=-1) {
os.write(su);
}
System.out.println("크롤링 완료");
// if(br!=null)br.close();
// if(isr!=null)is.close();
if(is!=null)is.close();
if(os!=null)os.close();
// if(pw!=null)pw.close();
// if(fw!=null)fw.close();
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
소켓통신
Client
public class Client extends Frame implements ActionListener{
TextField tf = new TextField();
static TextArea ta = new TextArea();
static PrintWriter pw;
public Client() {
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
add(ta, BorderLayout.CENTER);
add(tf, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
tf.addActionListener(this);
setBounds(100,100,300,400);
setVisible(true);
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String msg = tf.getText();
pw.println(msg);
pw.flush();
tf.setText("");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Client client = new Client();
String url = "192.168.240.119";
int port = 8080;
Socket sock = null;
InputStream is = null;
OutputStream os = null;
InputStreamReader isr = null;
OutputStreamWriter osw = null;
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
sock = new Socket(url, port);
is = sock.getInputStream();
os = sock.getOutputStream();
isr = new InputStreamReader(is);
osw = new OutputStreamWriter(os);
br = new BufferedReader(isr);
pw = new PrintWriter(osw);
String msg = null;
while(true) {
msg = br.readLine(); // 계속 읽어오는데
if(msg.equals("exit"))break;
ta.append(msg + "\n"); // 읽어온 값을 ta에 넣어주는 것
}
if(pw!=null)pw.close();
if(br!=null)br.close();
if(osw!=null)osw.close();
if(isr!=null)isr.close();
if(os!=null)os.close();
if(is!=null)is.close();
if(sock!=null)sock.close();
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Server
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<PrintWriter> list = new ArrayList<PrintWriter>();
ServerSocket serve = null;
try {
serve = new ServerSocket(8080);
while (true) {
final Socket sock = serve.accept();
Thread thr = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
InputStream is = null;
OutputStream os = null;
InputStreamReader isr = null;
OutputStreamWriter osw = null;
BufferedReader br = null;
PrintWriter pw = null;
InetAddress addr = null;
try {
addr = sock.getInetAddress();
is = sock.getInputStream();
os = sock.getOutputStream();
isr = new InputStreamReader(is);
osw = new OutputStreamWriter(os);
br = new BufferedReader(isr);
pw = new PrintWriter(osw);
list.add(pw);
String msg = null;
while((msg=br.readLine())!=null) {
msg = "["+addr.getHostAddress()+ "]" +msg;
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
PrintWriter w = list.get(i);
w.println(msg);
w.flush();
}
System.out.println(msg);
}
if(pw!=null) pw.close();
if(br!=null) br.close();
if(osw!=null) osw.close();
if(isr!=null) isr.close();
if(is!=null) is.close();
if(os!=null) os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
thr.start();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}'회고록(TIL&WIL)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| TIL 2023.01.06 리눅스 (0) | 2023.01.16 |
|---|---|
| WIL 2023.01.05 ~ 2023.01.06 통신, 네트워크 (0) | 2023.01.16 |
| WIL 2022.12.26 ~ 2022.12.30 java 공부 (0) | 2023.01.02 |
| TIL 2022.12.28 내가 쓰는 단축키 모음집 (0) | 2022.12.28 |
| WIL 2022.12.19 ~ 2022.12.23 java 공부 (1) | 2022.12.23 |

